Over the past few decades, more and more students have been learning online. However, the COVID-19 pandemic rapidly accelerated the adoption of digital learning across all age groups.
As the virus swept countries all over the world, children and adults alike were put into lockdown, which meant they needed to work and learn from home. This dramatically expanded the use of digital learning, with more than 1.2 billion children worldwide learning remotely, and many millions of employees also undertaking workplace learning online.
Digital learning during the pandemic was enabled through a variety of different technologies, many of which remain popular today. A thorough understanding of digital learning is essential for any modern degree-qualified educator, including understanding the benefits of digital learning.
What is digital learning?
Digital learning covers a wide array of techniques, tools and frameworks. Overall, digital learning is any type of learning or instructional practice in which technology is used as a learning aid.
Digital learning can be done completely online or blended with in-person learning; for example, it can include a digital element and real-life practice or a workshop.
Digital learning emerged in the 1990s when companies began to create online learning tools for their employees to use on their personal computers. This quickly gave way to e-learning delivered via learning management systems (LMSs), which became much more popular with the rise of the internet in the late 1990s and early 2000s, especially via the software Blackboard.
Since then, educational technology has grown and been adopted in numerous settings. Even before the pandemic, the ed tech market was huge and growing, worth US $18.66 billion (AU$27.73) in 2019. Popular products included language apps, video conferencing, and online tutoring.
How did the COVID-19 pandemic impact digital learning?
Since the pandemic, digital app use has grown exponentially. Many experts believed that little training in online learning, poor bandwidth and lack of preparation would cause many users to feel frustrated by online learning and refuse to adopt it.
However, the opposite was the case. Research shows that the total number of enrolments in online learning more than doubled. For example, in 2019, the online learning platform Coursera had 90 million learners enrolled in their courses; by 2021, that number had jumped to 189 million.
Types of digital learning
There are types of digital learning available for different educational styles, types and methods. Here are some types of digital learning:
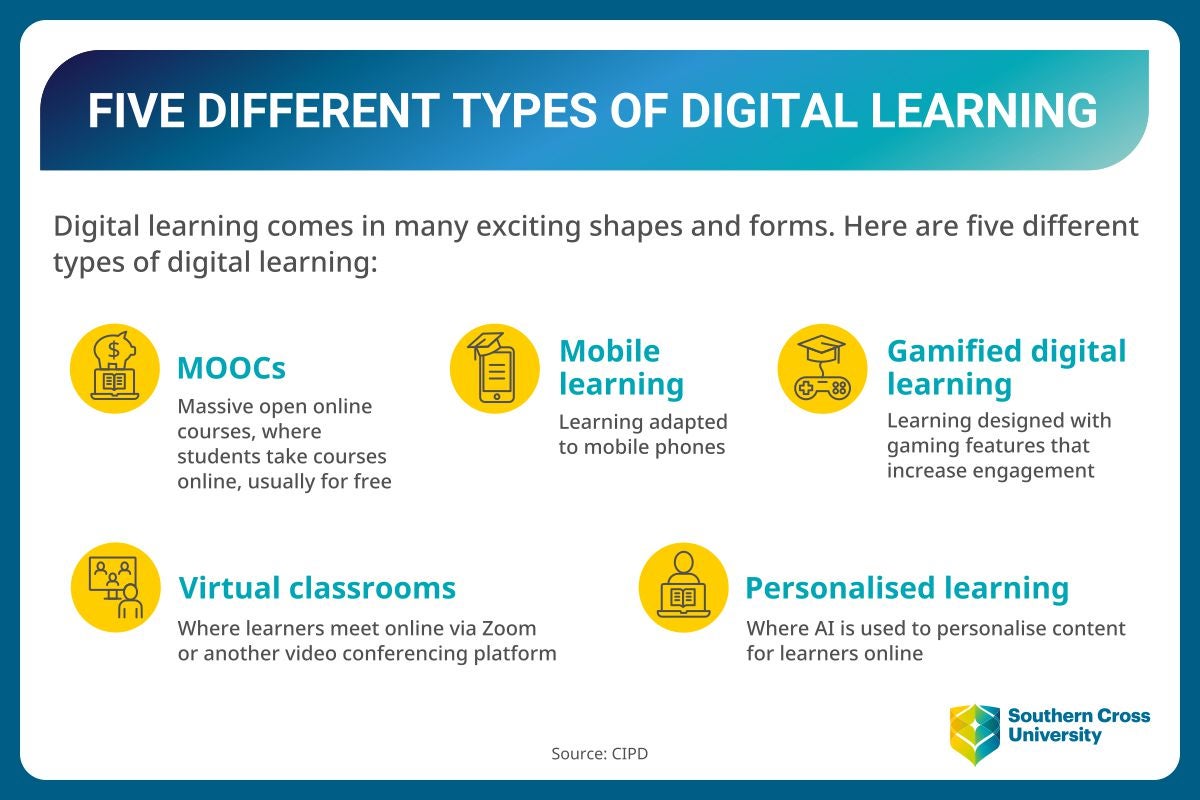
Virtual classrooms
The virtual classroom is defined as a digital classroom where educators and learners meet and engage with each other online. A virtual classroom typically includes video conferencing, and may also encompass features such as interactive activities, online assignments, quizzes and discussion forums.
MOOCs
MOOCs (massive open online courses) are open-access online courses, meaning that anyone with an internet connection can access them. They enable people from all over the world to participate in learning, even at some of the world’s best universities, for free or for a heavily discounted price.
People can take MOOCs on many subjects to gain a variety of skills and knowledge. Potential subjects include (but are not limited to) banking and finance, coding, science, management, art, design, education, engineering, languages and more.
Mobile learning
With the rise in mobile phone use (the average Australian currently spends 5.5 hours per day on their smartphone), people are increasingly turning to their phones for learning.
Mobile learning, or m-learning, is learning that takes place across multiple contexts through social, content or technology interactions using smartphone devices. It is touted as convenient and easy for most users.
Social and collaborative digital learning
Social and collaborative digital learning are formats in which students interact socially and collaborate, as well as work closely with educators. This collaboration may happen online or in the real world as learners work together to expand their knowledge of a particular topic.
What is a digital learning environment?
A digital learning environment (DLE) is a student-centred framework in which digital resources, technologies and applications allow learners to access educational resources at any time and from anywhere.
In an ideal world, a digital learning environment is used not only to deliver content but also to enable better interaction and collaboration between learners and educators and to ensure that learners meet their learning objectives.
Synchronous learning vs asynchronous learning
Digital learning opens up many opportunities for education delivery and scheduling, which can help learners who have location restrictions or other commitments that make strict education schedules inaccessible. To provide educational opportunities for those who need more flexibility, digital learning opportunities can be synchronous and asynchronous, or some mixture of the two.
Synchronous learning involves the delivery of education in real time. Synchronous educational environments usually use web conferencing tools and software for lecture delivery, interactive discussions, or activities that occur at scheduled times.
Asynchronous learning, on the other hand, does not need to occur at the same place or same time. Asynchronous educational environments may include online discussion forums, activities or assignments that students can complete at their own pace or by a certain deadline.
Many digital learning environments feature both asynchronous and synchronous elements, which are often called blended or hybrid learning. These educational environments may feature lectures and discussions, along with assignments, discussions, or activities that are completed independently.
What are the benefits of digital learning?
Digital learning’s exponential growth means that every modern educator needs to understand its benefits. Since digital learning is vast, it has many potential uses and benefits for students, educators, employers, and institutions.

1. It makes personalised learning possible.
Personalised learning entails a varied curriculum that reflects the needs of each learner so that each learner can effectively learn in different ways and at their own pace. Digital learning enables this primarily through collecting and applying data. Learning apps measure what learners are and aren’t doing well, and recommend content and pathways based on this information.
2. It enables self-directed learning.
Learners—especially adults—prefer to be self-directed, insofar as they manage their own time, learning, and learning progress. Because most digital learning is available anytime and anywhere, students can choose when and how they learn for themselves and can progress as fast as they choose.
3. It provides more universal access to education.
Education can open up a lifetime of opportunities for children and adults alike. Research shows that young people who complete their schooling are more likely to transition into further education, and those who complete further education are more likely to earn higher wages. In sum, a good education sets people up for a better future.
However, a large proportion of the world does not have access to education. In 2019, 58 million primary school-age children did not have access to education.
There are many reasons for this, including a lack of suitably qualified teachers, schools too far from children’s homes and children being needed at home. Fortunately, digital learning can help to solve many of these issues.
Digital learning makes universal access to education possible in several ways. First, it offers children in remote areas a way to access vital primary and secondary education. Second, through online university and higher-level courses, learners can access a rich breadth of information and learn advanced skills.
4. It lets students learn at their own pace.
In the past, many on-campus university courses, and also some school education, were inaccessible for people who wanted to study part-time or had other commitments, such as caring for children or pursuing a professional sport.
One benefit of digital learning is that it enables students to learn on their own schedule, and at their own pace. They can learn full-time, part-time or on any timeline that suits them best.
5. It is collaborative in nature.
In today’s modern world, many learners are technology-savvy and are used to engaging with others and sharing content online.
Digital learning uses different technologies to enable collaboration, both between learners and between learners and educators. This collaboration can take place in many ways, including via online forums and online chat tools, and it helps learners to form connections and broaden their horizons.
6. It creates an environment that aligns with a technology-rich world.
Regardless of an individual’s preferences, digital learning is prolific and is here to stay. Every day learners are surrounded by a wealth of technology that is increasingly being used in every facet of modern life.
For this reason, one of the most significant benefits of digital learning is that it creates an environment that empowers students to use technology that they already use in everyday life to learn.
6 keys to success in a digital classroom
A digital classroom is different from a traditional one in how it looks, feels and works. Modern educators should know these six keys to success in a digital classroom.
1. Use a digital learning selector.
With the breadth of learning technologies, tools and apps available, modern educators have a wealth of choices when it comes to digital learning — but that isn’t always a good thing. Sometimes, selecting the right technology can feel overwhelming and frustrating, and educators don’t know where to start.
Digital learning selectors help educators browse different available digital learning technologies to determine which is the best choice for them. They also offer filter options that allow educators to select technologies based on the complexity of what they are teaching.
Both the NSW Government and the Victoria State Government offer digital learning selectors to help educators find resources.
2. Understand which activities work best online versus in the classroom.
Digital learning technology has come a long way in terms of interactivity, but some things are simply better done in a face-to-face environment. Activities that may work best in a classroom setting are those that require students to make presentations or problem-solving activities that need to be completed as a group with real-time interaction.
3. Offer optimal course design.
Most traditional courses are presented in a linear format, but online courses don’t need to be structured in this manner. Instead, digital courses can use technologies such as algorithms and artificial intelligence (AI) to personalise learning based on what content students find most engaging, what they want to learn about and what areas they need support in.
4. Facilitate collaboration.
Like face-to-face learning, online learning can be passive, which is less effective than active, engaged learning. A key to success in a digital classroom is to ensure that tools and technologies encourage collaboration, whether through online forums, live chats, group activities or other types of collaboration between learners.
5. Provide various types of media.
Educators can engage students online using different types of media, such as videos, images, quizzes and presentations. To optimise engagement, educators should include a variety of types of media.
6. Embrace artificial intelligence.
Automating admin tasks, generation of assessments, and creating personalised learning plans are just some examples of how AI tools like ChatGPT are changing the future of education. While nothing will replace the connection and role of a teacher, it might be time to rethink traditional teaching practice and ask how we can integrate emerging software to benefit both the learner and the teacher.
Further resources
To learn more about how to succeed in a digital classroom, consider the following resources.
- TeachThought, “What Are the Keys to Effective Online Classroom Management?” — A comprehensive guide to how to effectively manage an online classroom
- Digital Learning Collaborative, “Six Strategic Steps to Digital Learning Success” — A guide for school leaders and educators
- Sizle, “10 Tips for Virtual Classroom Success” — Helpful tips for success in a digital classroom

Is digital learning the future of education?
With digital learning already so prevalent and its usage increasing year after year, many in the teaching and learning field are wondering if it will be the future of education.
Why digital learning will be a big part of the future
Current trends indicate that digital learning will likely play a large part in the future of education. The industry is growing at a staggering rate, with the digital learning market expected to be worth USD 77.23 billion by 2028 (AUD 112.83 billion), with a compound expected annual growth rate of 30.5%.
This growth will largely be driven by the increasing global adoption of smartphones, increased access to the internet and better technologies that enable engaging and enriching learning.
Other expected growth areas are increased uses for personalised learning and learning that include new technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and artificial intelligence (AI).
Why there is still a place for the traditional classroom
While there’s no doubt that digital learning continues to increase in popularity, there is still — and most likely will always be — a place for the traditional classroom. Especially for young children, there is no substitute for the engagement, collaboration and connection that face-to-face teachers provide.
This was evidenced during the coronavirus pandemic. Many students who learnt online for months during lockdowns are now substantially behind in their learning.
The future of education is (mostly) digital
From video conferencing tools to augmented reality, digital learning and the digital classroom have offered learners worldwide an abundance of exciting options for expanding their knowledge from the comfort of their bedroom or home office. During the coronavirus pandemic, digital education proved essential for both adult learners and children alike, as offices and schools were locked down. As digital learning continues to grow and thrive, online education seems poised to continue to complement face-to-face teaching and will offer an array of exciting possibilities.
If you want to enhance learner engagement through digital technologies while creating a supportive and inclusive environment, then SCU Online’s Master of Education may be for you.
Visit our website and download a course guide today to learn how to prepare for the future of teaching and advance your career.







